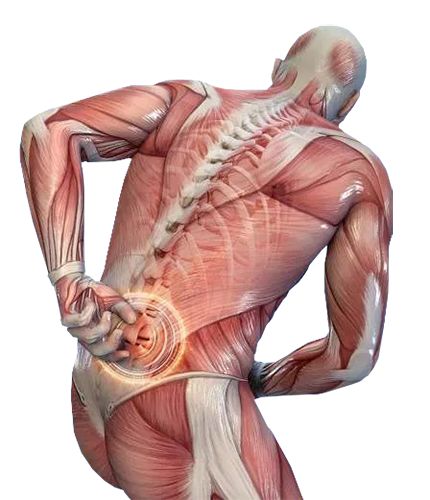
A muscle strain is different from a muscle tear, many people get these injuries confused. A strain is an injury that involves a muscle or tendon being overstretched. Your doctor may also call the injury a pulled tendon or muscle pull. (A tendon is the cord of tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone.)
Sometimes the injury is more severe, and one, a few, or all of the muscle fibers get torn. In this case, you have a muscle tear.
Symptoms and signs of muscle strain vs. muscle tear
Symptoms of muscle strains and muscle tears can be very similar, requiring a doctor to diagnose exactly what the injury is.
Symptoms of a muscle strain include:
- Tightness in the affected area
- Muscle spasms
- Weakness
- Cramping and immobility
- Pain
- Bruising or swelling
Doctors classify strains into three grades based on severity:
- Grade 1: This is a mild strain that affects only a small number of fibers in the muscle. It doesn’t cause any decrease in strength. You may feel pain and tenderness a day after sustaining the injury.
- Grade 2: This is a moderate strain, often characterized by the tearing of nearly half of the muscle fibers. You will experience acute pain (pain that comes on quickly but doesn’t last long) that is accompanied by swelling and a minor decrease in muscle strength.
- Grade 3: This is the same thing as a muscle tear, where your muscle is completely ruptured. The affected muscle may be torn in two or in such a way that it separates from the tendon. You will
experience a lot of pain and won’t be able to use the muscle or affected joint.
Symptoms of a muscle tear:
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Redness due to the injury
- Pain or weakness when the muscle or joint is used
- Inability to use the muscle
If you tear a muscle, you may hear a “pop” where the injury happened and notice a gap, dent, or other defects in the normal outline of the muscle.
Treatments for muscle strain vs. muscle tear:
Once a muscle strain or tear occurs, the muscle is vulnerable to reinjury. It is important to let the muscle heal properly and to follow preventive guidelines from your doctor. The most common method of treating a muscle strain is by applying a technique doctors call PRICE.
Protection: Protect the affected area from further injury — for example, by using a support.
Rest: Avoid exercise and reduce your daily physical activity. Using crutches or a walking stick may help if you can’t put weight on your ankle or knee. A sling may help if you’ve injured your shoulder.
Ice: Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every two to three hours.
Compression: Use elastic compression bandages during the day to limit swelling.
Elevation: Keep the injured body part raised above the level of your heart whenever possible. This may also help reduce swelling.
Resource ;https://www.myhealth1st.com.au/health-hub/articles/difference-between-strain-sprain/