Myofascial trigger points can cause chronic pain and affect a person’s range of motion. This can have a large impact on quality of life, mood, physical ability, and health. For this reason, individuals should always aim to identify and treat them early with Remedial Massage.
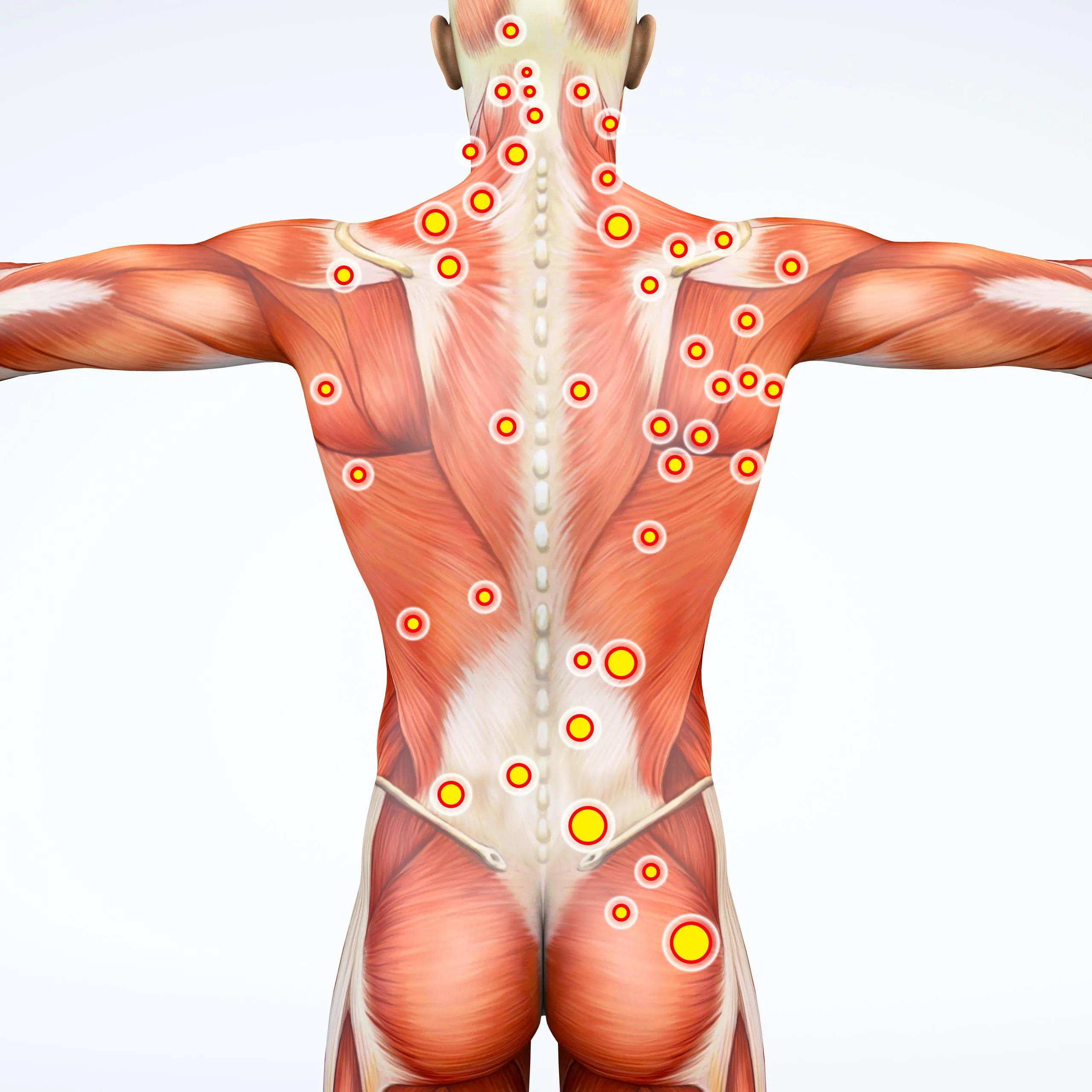
Myofascial trigger points are defined as “hyperirritable” nodules of muscle that can cause chronic pain, a decreased range of motion, referred pain, and autonomic dysfunction.
Trigger points are classified as either active or latent. With active trigger points, a person does not have to touch the trigger point itself for it to be painful. Latent trigger points are usually asymptomatic but become painful when touched.
Muscle knots can develop almost anywhere on the body where muscle or fascia is present.
Places where muscle knots commonly occur include:
- calf muscles
- lower back
- mid back
- neck
- shins
- shoulders
Through Remedial Massage, specifically trigger point therapy, these knots can be relieved.
Symptoms
Muscle knots feel like small, tender lumps or nodules, that a Remedial Massage Therapist can easily identify. They are palpable and can be felt when touched.
Symptoms of myofascial trigger points include:
- deep pain
- general numbness or tingling
- feelings of nerve pain
- a decreased range of motion
Trigger points often cause what doctors call referred pain. When a person presses on the trigger point, the pain spreads from the trigger point to nearby muscles.
A Remedial Therapist will treat not only the trigger point itself, but also the surrounding muscles that tighten as a result of the trigger point.
One of the most common sources of muscle knots is the trapezius muscle. This muscle makes a triangle-like shape from the neck to the middle of the back and the shoulder.
Tension and knots in the trapezius muscles often occur due to stress and poor posture.
Muscle knots can also cause additional symptoms, including:
- jaw pain
- lower back pain
- tension headaches
Causes
Common causes of muscle knots include:
- stress and tension
- physical trauma
- muscle injury
- emotional stress
- poor posture
- prolonged bed rest or sitting without stretching
A person who spends a significant amount of time sitting at work may develop muscle knots due to staying in the same position for prolonged periods.
Risk factors
Doctors have identified several risk factors for people more likely to experience trigger points. These include:
- history of joint problems and injuries
- biomechanical imbalance
- being overweight or having obesity
- difficulty sleeping or insomnia
- poor posture
- abnormal breathing mechanics
- sedentary lifestyle
Additionally, poor postural alignment due to cell phone use and improper sleeping and sitting positions may contribute to the development of muscle knots.
Through Remedial Massage treatment, poor postural alignment can be improved as the tension and trigger points are relieved.