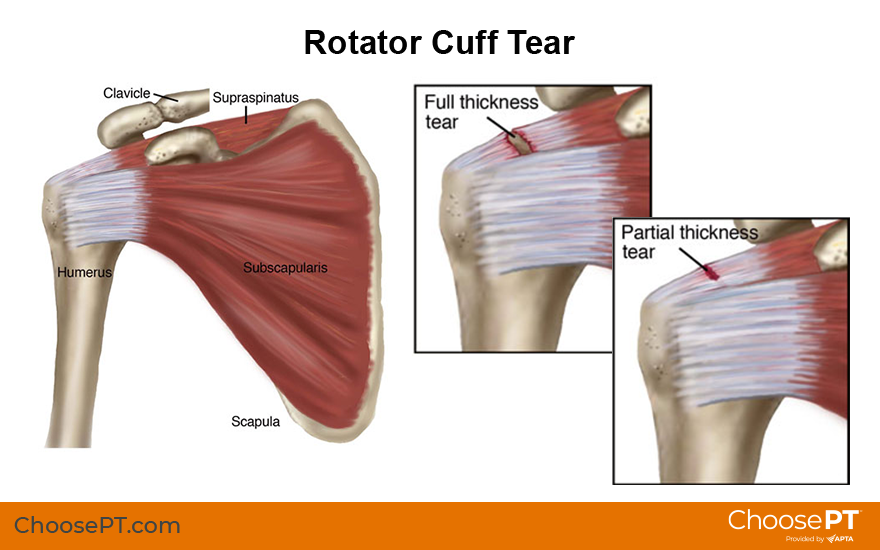
An infraspinatus tendon tear is a rotator cuff injury where the infraspinatus tendon , which helps with external rotation of the arm , is torn. Tears can be partial or complete, and may result from repetitive stress, trauma, or degeneration. Symptoms include pain, especially when sleeping, weakness in the affected arm, and difficulty with external rotation. Treatment options range from conservative approaches like rest, ice, NSAIDs, and physical therapy to surgical intervention for severe cases.
Causes:
- Overuse: Repetitive overhead motions can strain the tendon, leading to tears, especially in athletes.
- Trauma: Acute injuries like falls, shoulder dislocations, or clavicle fractures can cause tears.
- Degeneration: Age-related wear and tear can weaken the tendon, making it more susceptible to tearing.
Chronic Shoulder Instability: Long-term instability in the shoulder joint can put stress on the infraspinatus tendon.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Often localized in the shoulder, potentially radiating down the arm.
- Weakness: Difficulty lifting or rotating the arm.
- Painful Movements: Specific motions, like external rotation, may be painful or difficult.
- Clicking or Popping: A feeling of something “catching” in the shoulder during movement.
-
Physical Examination:Doctors will assess the range of motion, strength, and pain with specific movements, like the external rotation test (see below).
-
Imaging:X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the extent of the tear.
-
Conservative:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain.
- Ice: Applying ice to the shoulder to reduce inflammation.
- NSAIDs: Pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help with pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve range of motion.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical:
- Repair: For complete tears or tears that don’t respond to conservative treatment, surgery to repair the tendon may be necessary.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgical technique using a small camera and tools to repair the tear.
-
Positive Test:Weakness or pain during external rotation, especially if there’s no pain with other shoulder movements, can indicate an infraspinatus tear.