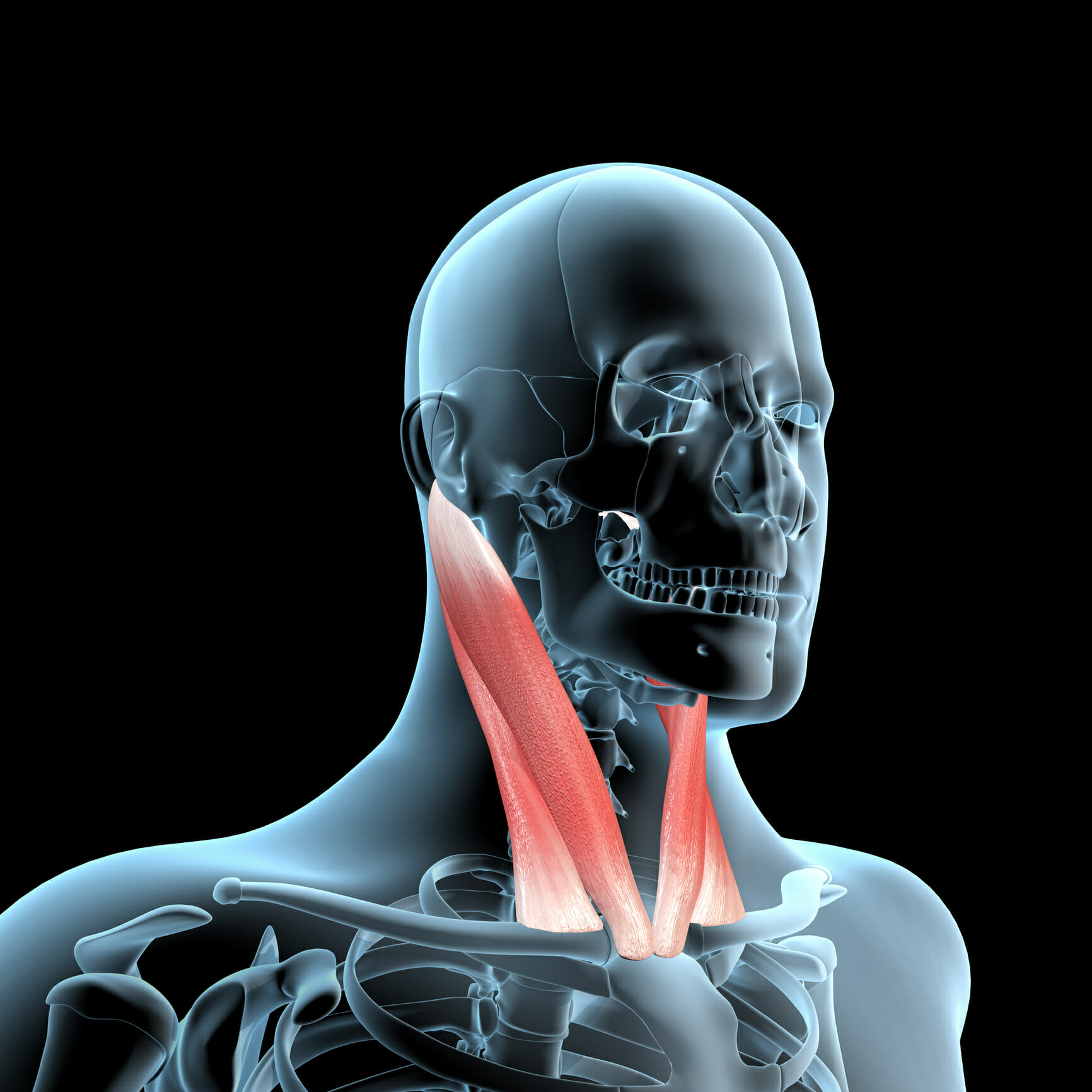
The SCM , is one of over 20 pairs of muscles acting on the neck. The SCM has dual innervation and multiple functions. It is a superficially palpable muscle with importance as an anatomical landmark within the neck region and as part of neuromuscular pathologies such as torticollis
It’s a paired muscle (two parts). Your SCM muscle starts at the bottom of your neck, wraps around both sides and ends at the base of your skull. It gets its name from its location and its parts.
- Sterno means your sternum, or breastbone. One part of the SCM muscle (the sternal head) begins at your breastbone. It travels up both sides of your neck, where it merges with the other part of the SCM muscle, the clavicular head.
- Cleido means your clavicle, or collarbone. The other part of the SCM muscle (the clavicular head) begins in the center of your left and right collarbones. It travels up both sides of your neck and merges with the sternal head.
- Mastoid is short for a section of bone called the mastoid process. The mastoid process is located at the base of your skull behind your ears. The SCM muscle ends at the mastoid process.
Function:
Your sternocleidomastoid helps you bend your neck and turn and tilt your head. It activates when you:
- Turn your head to face left or right.
- Tilt your head toward your right or left shoulder.
- Tilt your head backward, chin up.
- Tilt your head forward, chin to chest.
Your SCM muscle also helps you:
- Maintain your posture –It helps stabilize your neck even when you’re not moving.
- Breathe –Â It works with other neck muscles to lift your breastbone and collarbone when you inhale. The movement creates space for your lungs to take in air.
- Chew – It supports the joint that connects your jaw to your skull called the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The TMJ allows you to open and close your mouth.
Where do you feel SCM pain?
You may feel a dull or sharp pain within your SCM muscle. Commonly, people experience referred pain. This means that although the pain starts within the SCM muscle, you feel it in a different place.
The SCM muscle may cause pain in your:
- Face.
- Forehead.
- Eyes.
- Cheek.
- Ears.
- Sinuses.
- Throat (when you swallow).
- Shoulders.
 Treatments to help with SCM pain :
Massage, stretching, physical therapy and osteopathic manipulation. You can care for your SCM by managing stress and maintaining good posture.